1. The Primary Functions of Microporous Boards in the Steel Industry
– Minimize heat loss and reduce energy consumption
– Enhance the working environment within the facility
– Extend the operational life of equipment
– Decrease the thickness of insulation layers, allowing for increased internal volume or more compact equipment design
– Lower heat retention within the insulation layer, improving the speed of temperature rise.
2. Application Introduction
2.1 Steel Ladle
Usage Instructions:
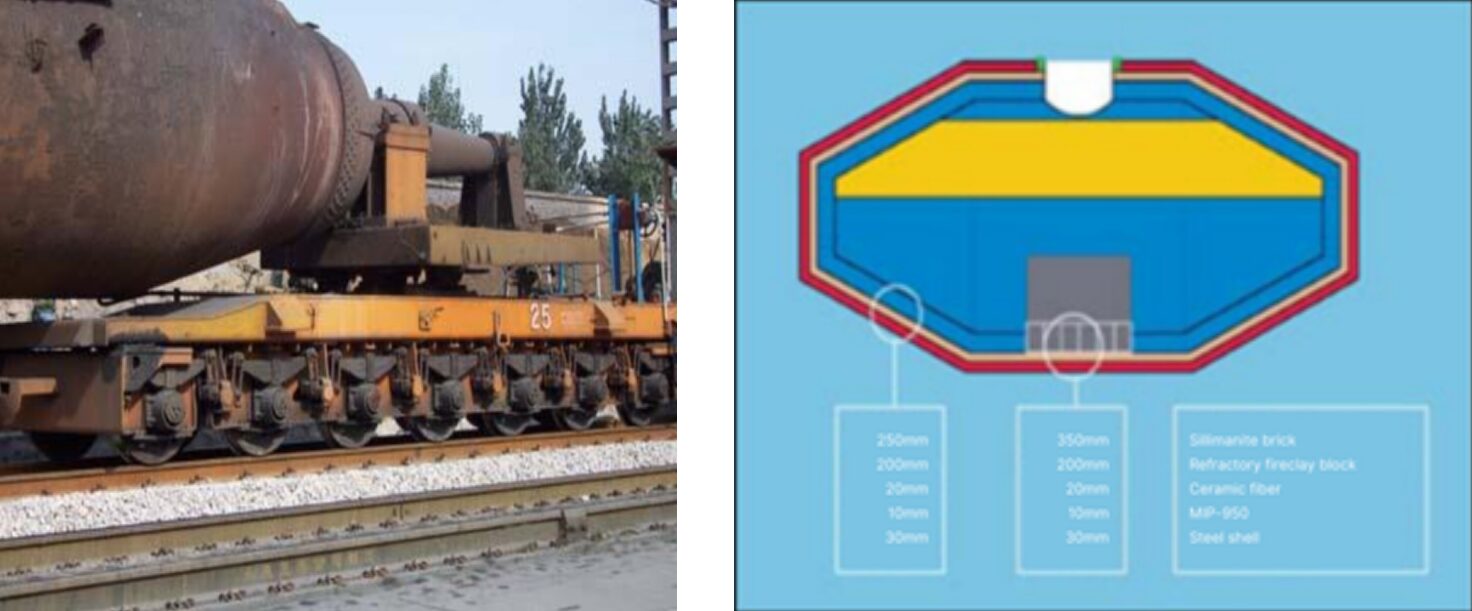
First, clean the inner walls of the ladle thoroughly. Apply a layer of adhesive to the ladle wall, then install the MIP-950S insulation layer. Afterward, construct the permanent and working layers in sequence.

Figure 1: Installation Construction on the Ladle
Benefits of Using Microporous Boards:
1) Reduces heat loss from the ladle shell.
2) Lowers the temperature of steel exiting the converter.
3) Decreases the heat needed for ladle preheating.
4) Lowers the ladle shell temperature, increasing its durability and safety.
5) Replaces thick insulating bricks, allowing the ladle to hold more molten steel.
6) Reduces temperature fluctuations affecting the refractory bricks, extending their service life.
7) Lowers consumption of permanent layer materials, reduces ladle weight, eases the load on lifting devices, and enhances safety.
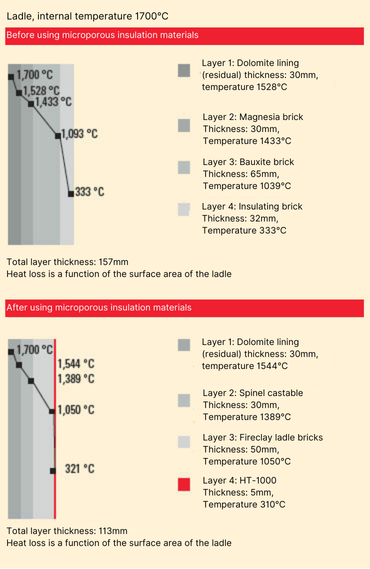
It is also noteworthy that some domestic steel plants are using composite nano-reflective insulation boards. While these materials have contributed to improved insulation and heat retention, they still lag behind nano-porous insulation materials in key areas such as thermal conductivity, thermal shrinkage, and specific heat capacity. The following outlines the differences between the two materials for customer reference.
Table 1: Comparison between Microporous Board and Composite Reflective Insulation Board

2.2 Tundish
Method of Use: Place a 5-10mm layer of insulating board on the inner side of the ladle, ensuring it avoids the steel nails on the ladle wall. Then, install the castable material (Figure 3).
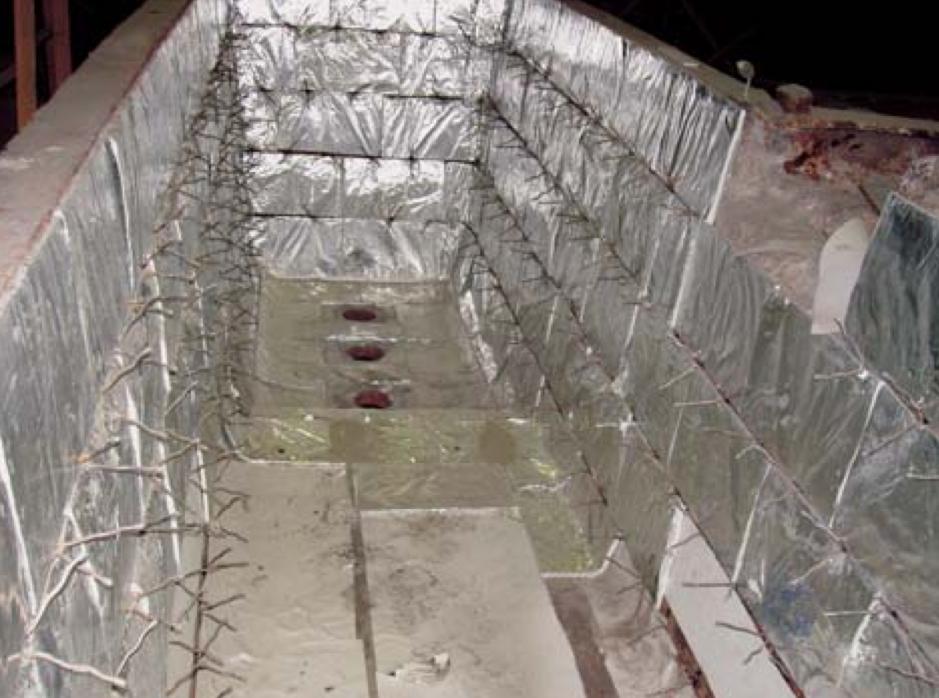

Figure 3: Installation Process on the Tundish
Effectiveness: This method helps reduce heat loss during continuous casting, stabilize molten steel temperatures, and improve the quality of continuous casting.
2.2 Torpedo Casing
Usage: Apply a 5-10mm insulating layer on the inner side of the torpedo casing, followed by laying firebrick (Figure 4).
Effectiveness: This reduces heat loss during iron transport, raises the temperature of iron reaching the converter by approximately 40°C, lowers energy consumption, and creates favorable conditions for dephosphorization treatment during torpedo casing transport.
2.3 Hot Air Pipeline
Usage: Install multiple layers of roller blind-style insulation material inside the pipeline, followed by the installation of firebricks or castables.
Effectiveness: This minimizes heat loss, increases the temperature of the hot air entering the blast furnace, and boosts the efficiency of the hot blast stove.
2.4 RH Degassing Unit
Method of Use: Attach the nano-porous insulating board (5-10mm) to the inner side of the furnace wall, then install the castable material.
Effectiveness: This reduces heat loss in the molten steel during the circulation process.

2.5 Step-Type Heating Furnace Water-Cooled Colum
Method of Use: Wrap two layers of 5mm thick soft felt around the water-cooled pipe and secure them before installing the casting material.
Effectiveness: Compared to ceramic fiber insulation, this reduces the amount of heat removed by cooling water by approximately 24%. As nearly 15% of the energy in a step-type heating furnace is lost through cooling water, using nano-porous insulation significantly enhances energy efficiency.
3. Key Features of Microporous Boards
– Superior Thermal Insulation: With thermal conductivity 3-4 times lower than conventional materials, microporous insulation significantly reduces energy consumption, minimizes insulation layer thickness and weight, and increases the effective capacity of equipment.
– Outstanding Thermal Properties: It offers low specific heat, minimal heat retention, and excellent resistance to thermal shock, ensuring long-term use without damage from external forces.
– Eco-Friendly: Free from harmful fibers, this material meets both domestic and international environmental regulations.
– Easy Installation: In ladle applications, it can be easily affixed using tape or refractory mortar.
– Non-Combustible: The material is fire-resistant, providing an extra layer of safety in high-temperature environments.

4. Conclusion
As the application technology of nano-porous insulation materials continues to mature, their successful implementation in some foreign steel plants in recent years has proven the material’s significant role in energy conservation and emission reduction. With the decrease in material costs, enhanced awareness of energy conservation and environmental protection among enterprises, and the improvement of relevant national standards, the application of nano-porous insulation materials in the steel industry is expected to become increasingly widespread.
Stay Connected
For live updates and behind-the-scenes content, follow us on:
- LinkedIn: Firebird LinkedIn
- YouTube: Firebird YouTube
- Facebook: Firebird Facebook
- Website: Firebird main website


